The move to SAP S/4HANA introduces the business partner as the central master data object, replacing traditional customer and supplier data. All customers and vendors must be converted to business partners for a successful transition. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the end-to-end process of business partner in SAP S/4HANA.
Table of Contents
Overview of Business Partner
Business partner in SAP S/4HANA is the leading object for managing master data. Customer and supplier data from SAP ERP must be converted to BP during the move to S/4.
Compared to traditional ERP transactions, managing Customer and Supplier master data through the Business Partner feature offers several advantages, including:
- The ability to manage multiple addresses along with their respective address usages.
- Unlike classical transactions where a customer is linked to a single account group, Business Partner allows for multiple roles to be associated with the same Business Partner.
- Enhanced data sharing and reusability, simplifying data consolidation efforts.
- Availability of general data for all Business Partner roles, with role-specific data stored separately.
- Flexibility in maintaining multiple relationships with a single Business Partner.
- Capability to manage time-dependent information across various sub-entities like roles, addresses, relationships, and bank data.
Business Partner/CVI Conversion Process
Business Partner is capable of centrally managing master data for business partners, customers, and vendors. Here are some key points:
- BP is the single point of entry to create, edit, and display master data for business partners, customers, and vendors.
- All customers and suppliers, including contacts with the deletion flag, must become BPs even if they already exist in your system.
- CVI (Customer Vendor Integration) is the standard process for converging customer and supplier data to BP.
Proper setup of customizing and mappings is crucial prior to conversion. The CVI cockpit guides you through the activities in sequence. For an ECC system, the CVI Cockpit can be launched via transaction code – CVI_COCKPIT.
With retail customers, there are additional steps required so review SAP Note 2310884.
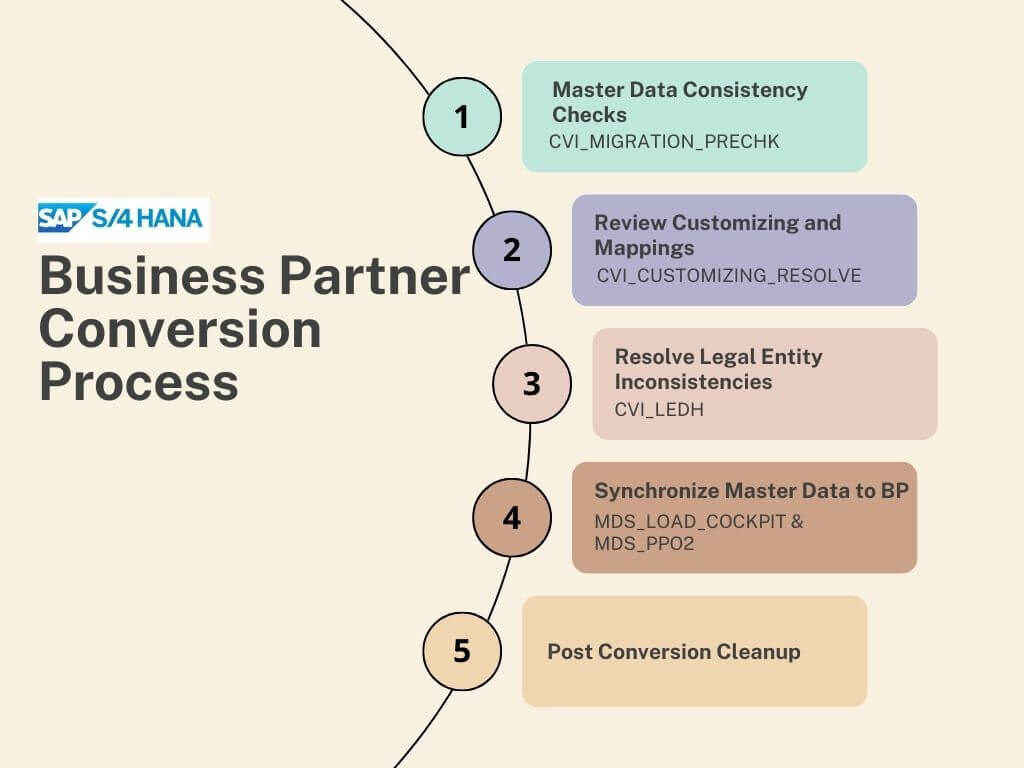
Now let’s walk through the end-to-end process for converting your master data to business partner.
Step 1: Master Data Consistency Checks
Before starting any conversion activities, it is important to identify and fix any data inconsistencies in SAP ECC system. Run the CVI_MIGRATION_PRECHK report or use transaction code CVI_PRECHK to check:
- Tax codes
- Postal/ZIP codes
- Email addresses
- Bank details
- Tax jurisdictions
- Industries
- Addresses
- Number ranges
- Transportation Zone
For contact persons, it will validate postal code, email, and address.
Review the output listing any errors found. You must fix these in your current customer/supplier master records before conversion will work properly.
Step 2: Review Customizing and Mappings
There are a number of customizing settings and mappings that must be correctly setup for business partner conversion.
Use the CVI_CUSTOMIZING_RESOLVE program to check for missing entries and create any that are needed. Some key areas to check are:
- Activating BP synchronization
- Enabling customer/supplier to BP sync
- Post processing setup
- Number range settings
- Mapping account groups to BP roles
- Contact person attribute mappings
- Industry mappings
- Legal form/status mappings
To allow the customer/supplier numeric numbers to be taken over to the business partner, the numeric intervals of the business partner number ranges must be set to external.
CVI Mapping Tables
The pre-check process in CVI involves a comparison of all entries in KNA1/LFA1 with those in the mapping tables CVI_CUST_LINK and CVI_VEND_LINK.
When it comes to contacts associated with established KNA1/LFA1 entries, this pre-check logic extends to the comparison of all KNVK entries linked to customers (using field KUNNR) and suppliers (using field LIFNR) with the entries present in the mapping tables CVI_CUST_CT_LINK and CVI_VEND_CT_LINK.
Step 3: Resolve Legal Entity Inconsistencies
Sometimes you may have customer and supplier records representing the same legal entity but with inconsistent address, tax or bank data.
The CVI_LEDH report allows you to select the leading entity for a legal entity pair. This ensures the data is harmonized properly for conversion.
Run the report and choose Customer or Vendor as the leading record for any inaccurate fields.
Step 4: Synchronize Master Data to BP
Now you are ready to convert! Use the MDS_LOAD_COCKPIT report to synchronize customer and supplier data to corresponding business partners.
In the selection screen, choose:
- Source object: Customer or Supplier
- Target object: Business Partner
- Scope and number range filters as needed
Execute the report. Check for any errors in the monitor tab and resolve inconsistent data based on the error messages.
If needed, you can view additional error details in the MDS_PPO2 transaction. Fix the data and reset the error status to complete.
Rerun MDS_LOAD_COCKPIT until all records synchronize successfully.
Step 5: Post Conversion Cleanup
Once your master data is converted to business partner, there are some final steps:
- Disable any temporary mapping logic or suppression of checks configured for the migration.
- Adjust business partner number ranges back from external to internal.
- Set customer/supplier number ranges to external to allow identical numbers.
- Run reconciliation reports to validate successful conversion.
This completes the key steps for migrating your customers and vendors to central business partners in S/4HANA. With proper preparation and setting up mappings, the conversion process can go very smoothly.
Tips for Business Partner Conversion Project
Here are some additional tips when planning your business partner in SAP S/4HANA conversion project:
- Check for retail customer mappings separately.
- Allow sufficient time based on volume of customer/supplier data.
- Start early and schedule cutover/downtime appropriately.
- Involve both technical and business teams.
- Cleanse data before conversion if time permits.
- Freeze any master data changes during conversion process.
- Capture exception records that fail conversion for follow-up.
- Validate results and reconcile converted totals.
Business Partner Transactions in S/4HANA
With business partner as the leading master data object, you will use different transactions to maintain business partner in SAP S/4HANA:
- BP: General business partner maintenance
- BP_ROLE: Maintain business partner roles
While customer and supplier data can still be viewed separately, all underlying updates must go through the central BP record. Below transaction codes are not available in SAP S/4HANA and get redirected to transaction – BP (Maintain Business Partner)
FD01,FD02,FD03, FK01,FK02,FK03,MAP1,MAP2,MAP3, MK01, MK02, MK03, V-03,V-04,V-05,V-06,V-07,V-08,V-09, V-11, VAP1, VAP2, VAP3, VD01, VD02,VD03, XD01, XD02, XD03, XK01, XK06, XK07, XK02, XK03
Along with above transaction codes, following transaction codes are obsolete in SAP S/4HANA:
- FD06 – Mark Customer for Deletion (Accounting)
- FK06 – Mark Vendor for Deletion (Accounting)
- MK06 – Mark vendor for Deletion (Purchasing)
- MK12 – Change vendor (Purchasing), planned
- MK18 – Activate planned vendor changes (Purchasing)
- MK19 – Display vendor (purchasing), future
- VD06 – Mark customer for deletion (sales)
- XD06 – Mark customer for deletion (central)
- V+21 – Create Sales Prospect
- V+22 – Create Competitor
- V+23 – Create Business Partner
Key Benefits of Business Partner
Using business partner in SAP S/4HANA as the primary master data entity provides a number of key benefits:
- Single point of maintenance for customer, supplier and contact data
- Consistent data for legal entities acting as both customer and supplier
- Central data storage independent of application transactions
- Reduced data redundancy and risk of inconsistencies
- Simplified integration across SAP applications
- Enhanced reporting with single view of all business partners
With a thoughtful implementation approach, you can achieve a smooth transition to centralized master data management with business partner in SAP S/4HANA.
Business Partner in SAP S/4HANA
Here are some key points to note when using certain SAP S/4HANA functionalities related to business partners:
- When creating a consumer, use the BP Grouping associated with the consumer account group in TBD001. The customer itself is a contact person, so no further relationships can be maintained.
- When creating a one-time customer or supplier, use the BP Grouping associated with the one-time customer/supplier account group in TBD001 and TBC001.
- Avoid using the IDocs DEBMS/CREMAS and CREMAS for data integration between S/4HANA systems. Use Business Partner web services via API Business Hub instead. Only use IDocs if the source system has Customer/Supplier master data without Business Partners.
- You can maintain role validity for Business Partners in S/4HANA. This allows closing a role like prospect and changing to another like sold-to-party after a validity period. For example, a prospect role can be changed to sold-to-party by setting a validity period and closing the previous role.
Conclusion
Migrating your master data to the business partner model is a key milestone in your S/4HANA journey. By following the step-by-step guidance, you can ensure a smooth and successful conversion. With a clear understanding of the end-to-end process, the practical tips for planning, and details on setup and transactions, you’ll be well equipped to undertake this project.
The business partner provides a central hub for customer, supplier and contact data, eliminating fragmentation and inconsistencies. The result is cleaner master data and streamlined processes in S/4HANA. Whether you’re just starting to evaluate the move to S/4HANA or planning your conversion project, be sure to bookmark this guide as the go-to reference for your business partner transition. With the knowledge gained here, you can approach master data conversion with confidence.